PARKINSON DISEASE
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological movement disorder. Common symptoms include tremor, slowness of movement, stiff muscles, unsteady walk and balance and coordination problems. There is no cure for the disease. Most patients can maintain a good quality of life with medications. In some patients, surgery can help improve symptoms.
When to see a doctor
See your doctor if you have any of the symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease — not only to diagnose your condition but also to rule out other causes for your symptoms.
Causes
In Parkinson’s disease, certain nerve cells (neurons) in the brain gradually break down or die. Many of the symptoms are due to a loss of neurons that produce a chemical messenger in your brain called dopamine. When dopamine levels decrease, it causes abnormal brain activity, leading to impaired movement and other symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
The cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown, but several factors appear to play a role, including:
- Researchers have identified specific genetic mutations that can cause Parkinson’s disease. But these are uncommon except in rare cases with many family members affected by Parkinson’s disease.
However, certain gene variations appear to increase the risk of Parkinson’s disease but with a relatively small risk of Parkinson’s disease for each of these genetic markers.
- Environmental triggers.Exposure to certain toxins or environmental factors may increase the risk of later Parkinson’s disease, but the risk is relatively small.
Researchers have also noted that many changes occur in the brains of people with Parkinson’s disease, although it’s not clear why these changes occur. These changes include:
- The presence of Lewy bodies.Clumps of specific substances within brain cells are microscopic markers of Parkinson’s disease. These are called Lewy bodies, and researchers believe these Lewy bodies hold an important clue to the cause of Parkinson’s disease.
- Alpha-synuclein found within Lewy bodies.Although many substances are found within Lewy bodies, scientists believe an important one is the natural and widespread protein called alpha-synuclein (a-synuclein). It’s found in all Lewy bodies in a clumped form that cells can’t break down. This is currently an important focus among Parkinson’s disease researchers.
Risk factors
Age. Young adults rarely experience Parkinson’s disease. It ordinarily begins in middle or late life, and the risk increases with age. People usually develop the disease around age 60 or older.
Heredity. Having a close relative with Parkinson’s disease increases the chances that you’ll develop the disease. However, your risks are still small unless you have many relatives in your family with Parkinson’s disease.
Sex. Men are more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease than are women.
Exposure to toxins. Ongoing exposure to herbicides and pesticides may slightly increase your risk of Parkinson’s disease.
To diagnose Parkinson’s disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins
Symptoms
Parkinson’s disease signs and symptoms can be different for everyone. Early signs may be mild and go unnoticed. Symptoms often begin on one side of your body and usually remain worse on that side, even after symptoms begin to affect both sides.
Parkinson’s signs and symptoms may include:
- A tremor, or shaking, usually begins in a limb, often your hand or fingers. You may rub your thumb and forefinger back and forth, known as a pill-rolling tremor. Your hand may tremble when it’s at rest.
- Slowed movement (bradykinesia).Over time, Parkinson’s disease may slow your movement, making simple tasks difficult and time-consuming. Your steps may become shorter when you walk. It may be difficult to get out of a chair. You may drag your feet as you try to walk.
- Rigid muscles. Muscle stiffness may occur in any part of your body. The stiff muscles can be painful and limit your range of motion.
- Impaired posture and balance. Your posture may become stooped, or you may have balance problems as a result of Parkinson’s disease.
- Loss of automatic movements. You may have a decreased ability to perform unconscious movements, including blinking, smiling or swinging your arms when you walk.
- Speech changes. You may speak softly, quickly, slur or hesitate before talking. Your speech may be more of a monotone rather than have the usual inflections.
- Writing changes. It may become hard to write, and your writing may appear small.
IN ADVANCED CASES Of Parkinson’s disease is often accompanied by these additional problems, which may be treatable:
- Thinking difficulties. You may experience cognitive problems (dementia) and thinking difficulties. These usually occur in the later stages of Parkinson’s disease. Such cognitive problems aren’t very responsive to medications.
- Depression and emotional changes. You may experience depression, sometimes in the very early stages. Receiving treatment for depression can make it easier to handle the other challenges of Parkinson’s disease.
You may also experience other emotional changes, such as fear, anxiety or loss of motivation. Doctors may give you medications to treat these symptoms.
- Swallowing problems. You may develop difficulties with swallowing as your condition progresses. Saliva may accumulate in your mouth due to slowed swallowing, leading to drooling.
- Chewing and eating problems. Late-stage Parkinson’s disease affects the muscles in your mouth, making chewing difficult. This can lead to choking and poor nutrition.
- Sleep problems and sleep disorders. People with Parkinson’s disease often have sleep problems, including waking up frequently throughout the night, waking up early or falling asleep during the day.
People may also experience rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder, which involves acting out your dreams. Medications may help your sleep problems.
- Bladder problems. Parkinson’s disease may cause bladder problems, including being unable to control urine or having difficulty urinating.
- Many people with Parkinson’s disease develop constipation, mainly due to a slower digestive tract.
You may also experience:
- Blood pressure changes. You may feel dizzy or lightheaded when you stand due to a sudden drop in blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension).
- Smell dysfunction. You may experience problems with your sense of smell. You may have difficulty identifying certain odors or the difference between odors.
- Many people with Parkinson’s disease lose energy and experience fatigue, especially later in the day. The cause isn’t always known.
- Some people with Parkinson’s disease experience pain, either in specific areas of their bodies or throughout their bodies.
- Sexual dysfunction. Some people with Parkinson’s disease notice a decrease in sexual desire or performance.
Prevention
Because the cause of Parkinson’s is unknown, proven ways to prevent the disease also remain a mystery.
regular aerobic exercise might reduce the risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Some other research has shown that people who consume caffeine — which is found in coffee, tea and cola — get Parkinson’s disease less often than those who don’t drink it.
Green tea is also related to a reduced risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. However, it is still not known whether caffeine actually protects against getting Parkinson’s, or is related in some other way.
Currently there is not enough evidence to suggest drinking caffeinated beverages to protect against Parkinson’s.
Diagnosis
No specific test exists to diagnose Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor trained in nervous system conditions (neurologist) will diagnose Parkinson’s disease based on your medical history, a review of your signs and symptoms, and a neurological and physical examination.
Imaging tests — such as an MRI, ultrasound of the brain, and PET scans — also may be used to help rule out other disorders. Imaging tests aren’t particularly helpful for diagnosing Parkinson’s disease.
In addition to your examination, your doctor may give you carbidopa-levodopa (Rytary, Sinemet, others), a Parkinson’s disease medication. You must be given a sufficient dose to show the benefit, as low doses for a day or two aren’t reliable. Significant improvement with this medication will often confirm your diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.
Sometimes it takes time to diagnose Parkinson’s disease. Doctors may recommend regular follow-up appointments with neurologists trained in movement disorders to evaluate your condition and symptoms over time and diagnose Parkinson’s disease.
Treatment
Parkinson’s disease can’t be cured, but medications can help control your symptoms, often dramatically. In some more advanced cases, surgery may be advised.
Your doctor may also recommend lifestyle changes, especially ongoing aerobic exercise. In some cases, physical therapy that focuses on balance and stretching also is important. A speech-language pathologist may help improve your speech problems.
Medications may help you manage problems with walking, movement and tremor. These medications increase or substitute for dopamine.
People with Parkinson’s disease have low brain dopamine concentrations. However, dopamine can’t be given directly, as it can’t enter your brain.
You may have significant improvement of your symptoms after beginning Parkinson’s disease treatment. Over time, however, the benefits of drugs frequently diminish or become less consistent. You can usually still control your symptoms fairly well.
MEDICATION:
Medications your doctor may prescribe include:
- Carbidopa-levodopa.Levodopa, the most effective Parkinson’s disease medication, is a natural chemical that passes into your brain and is converted to dopamine.
Levodopa is combined with carbidopa (Lodosyn), which protects levodopa from early conversion to dopamine outside your brain. This prevents or lessens side effects such as nausea.
Side effects may include nausea or lightheadedness (orthostatic hypotension).
After years, as your disease progresses, the benefit from levodopa may become less stable, with a tendency to wax and wane (“wearing off”).
Also, you may experience involuntary movements (dyskinesia) after taking higher doses of levodopa. Your doctor may lessen your dose or adjust the times of your doses to control these effects.
- Inhaled carbidopa-levodopa.Inbrija is a new brand-name drug delivering carbidopa-levodopa in an inhaled form. It may be helpful in managing symptoms that arise when oral medications suddenly stop working during the day.
- Carbidopa-levodopa infusion.Duopa is a brand-name medication made up of carbidopa and levodopa. However, it’s administered through a feeding tube that delivers the medication in a gel form directly to the small intestine.
Duopa is for patients with more-advanced Parkinson’s who still respond to carbidopa-levodopa, but who have a lot of fluctuations in their response. Because Duopa is continually infused, blood levels of the two drugs remain constant.
Placement of the tube requires a small surgical procedure. Risks associated with having the tube include the tube falling out or infections at the infusion site.
- Dopamine agonists.Unlike levodopa, dopamine agonists don’t change into dopamine. Instead, they mimic dopamine effects in your brain.
They aren’t as effective as levodopa in treating your symptoms. However, they last longer and may be used with levodopa to smooth the sometimes off-and-on effect of levodopa.
Dopamine agonists include pramipexole (Mirapex), ropinirole (Requip) and rotigotine (Neupro, given as a patch). Apomorphine (Apokyn) is a short-acting injectable dopamine agonist used for quick relief.
Some of the side effects of dopamine agonists are similar to the side effects of carbidopa-levodopa. But they can also include hallucinations, sleepiness and compulsive behaviors such as hypersexuality, gambling and eating. If you’re taking these medications and you behave in a way that’s out of character for you, talk to your doctor.
- MAO B inhibitors.These medications include selegiline (Zelapar), rasagiline (Azilect) and safinamide (Xadago). They help prevent the breakdown of brain dopamine by inhibiting the brain enzyme monoamine oxidase B (MAO B). This enzyme metabolizes brain dopamine. Selegiline given with levodopa may help prevent wearing-off.
Side effects of MAO B inhibitors may include headaches, nausea or insomnia. When added to carbidopa-levodopa, these medications increase the risk of hallucinations.
These medications are not often used in combination with most antidepressants or certain narcotics due to potentially serious but rare reactions. Check with your doctor before taking any additional medications with an MAO B inhibitor.
- Catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors.Entacapone (Comtan) and opicapone (Ongentys) are the primary medications from this class. This medication mildly prolongs the effect of levodopa therapy by blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine.
Side effects, including an increased risk of involuntary movements (dyskinesia), mainly result from an enhanced levodopa effect. Other side effects include diarrhea, nausea or vomiting.
Tolcapone (Tasmar) is another COMT inhibitor that is rarely prescribed due to a risk of serious liver damage and liver failure.
- These medications were used for many years to help control the tremor associated with Parkinson’s disease. Several anticholinergic medications are available, including benztropine (Cogentin) or trihexyphenidyl.
However, their modest benefits are often offset by side effects such as impaired memory, confusion, hallucinations, constipation, dry mouth and impaired urination.
- Doctors may prescribe amantadine alone to provide short-term relief of symptoms of mild, early-stage Parkinson’s disease. It may also be given with carbidopa-levodopa therapy during the later stages of Parkinson’s disease to control involuntary movements (dyskinesia) induced by carbidopa-levodopa.
Side effects may include a purple mottling of the skin, ankle swelling or hallucinations.
Surgical procedures
Deep brain stimulation.
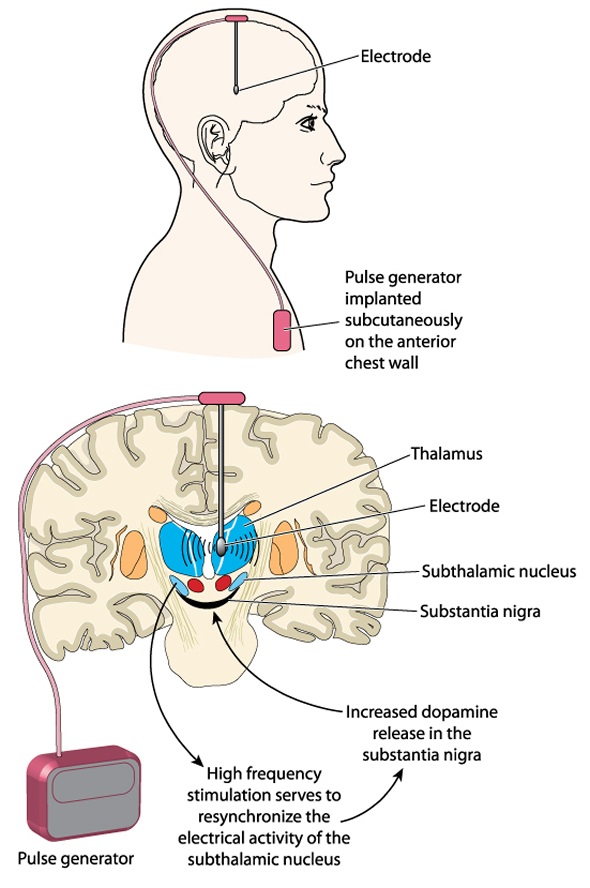
In deep brain stimulation (DBS), surgeons implant electrodes into a specific part of your brain. The electrodes are connected to a generator implanted in your chest near your collarbone that sends electrical pulses to your brain and may reduce your Parkinson’s disease symptoms.
Your doctor may adjust your settings as necessary to treat your condition. Surgery involves risks, including infections, strokes or brain hemorrhage. Some people experience problems with the DBS system or have complications due to stimulation, and your doctor may need to adjust or replace some parts of the system.
Deep brain stimulation is most often offered to people with advanced Parkinson’s disease who have unstable medication (levodopa) responses. DBS can stabilize medication fluctuations, reduce or halt involuntary movements (dyskinesia), reduce tremor, reduce rigidity, and improve slowing of movement.
DBS is effective in controlling erratic and fluctuating responses to levodopa or for controlling dyskinesia that doesn’t improve with medication adjustments.
However, DBS isn’t helpful for problems that don’t respond to levodopa therapy apart from a tremor. A tremor may be controlled by DBS even if the tremor isn’t very responsive to levodopa.
Although DBS may provide sustained benefit for Parkinson’s symptoms, it doesn’t keep Parkinson’s disease from progressing.
Because there have been infrequent reports that the DBS therapy affects the movements needed for swimming, the Food and Drug Administration recommends consulting with your doctor and taking water safety precautions before swimming.